문제 요약
문제 링크: 백준 1035 - 조각 움직이기
문제 설명
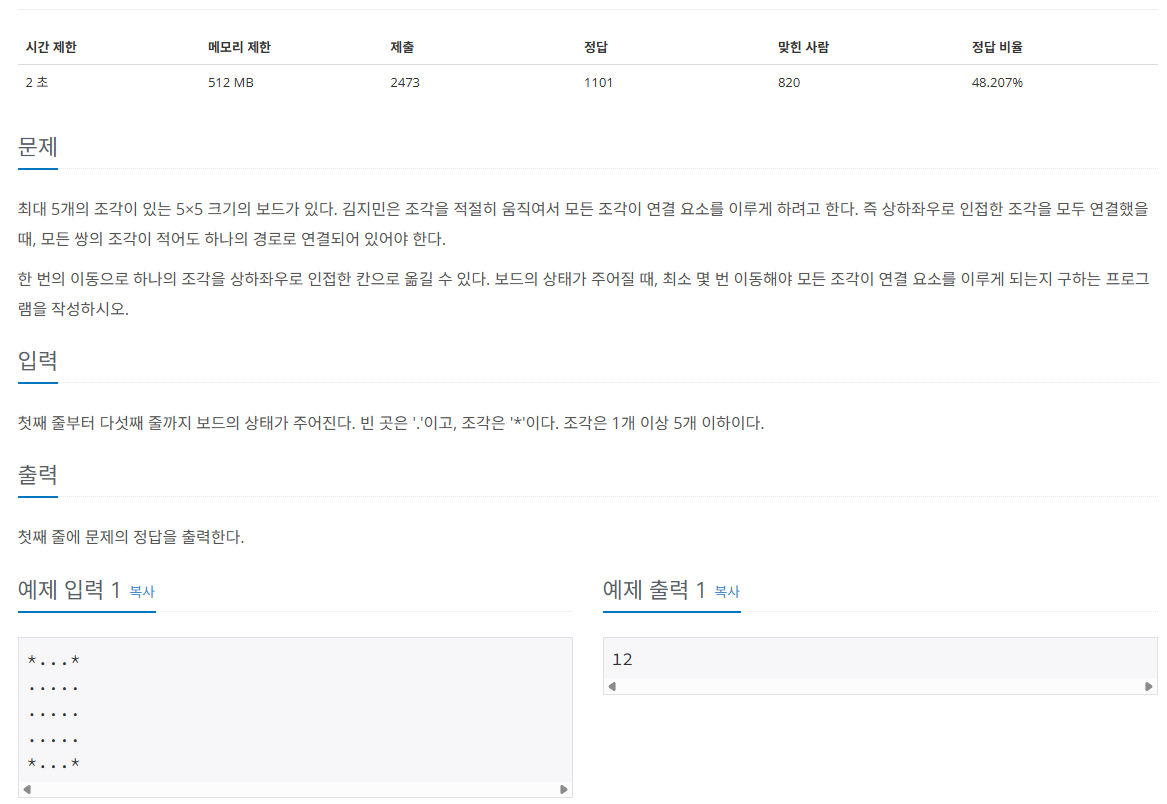

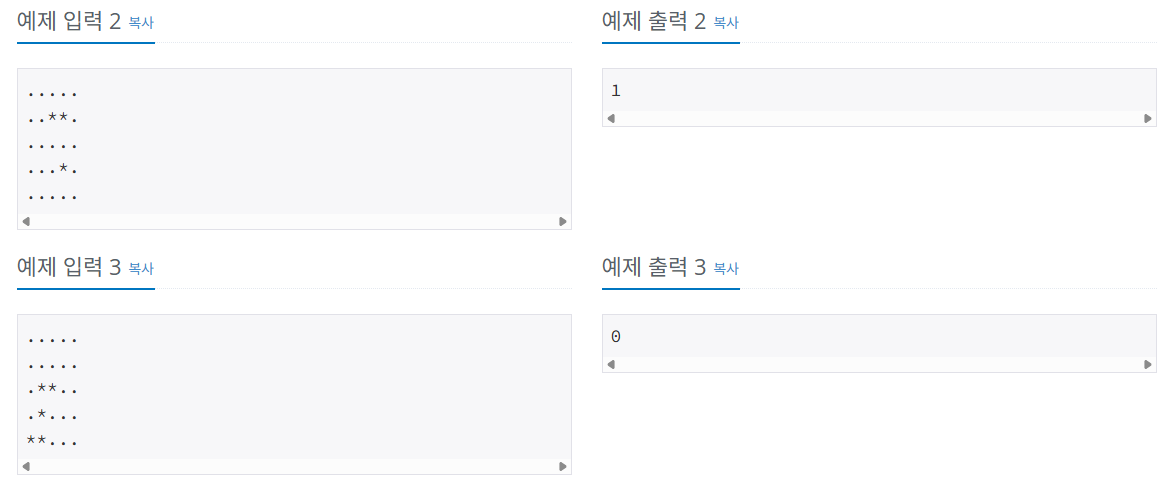
접근 방법
5X5 크기의 고정된 판에서 최대 5개의 조각의 모든 움직임 경우의 수를 구해준다. N이 크지 않아서 완전탐색 방법으로 해결하고자 시도했었다.
첫 번째 풀이로는 dfs로 조각이 이동할 수 있는 모든 경우의 수를 계산하여 그때, 조각끼리 연결되어 있다면, 조각들의 이동 값 중에서 가장 작은 값을 정답으로 저장할 수 있게 구현했다. 최적화 없는 이 방식으로도 통과가 되긴 했지만, 필자의 코드가 다른 코드들보다 실행시간이 유독 길었다.
따라서 두 번째 풀이에선 첫 번째 풀이에서 중복된 움직임 경우의 조각은 판단하지 않게 map을 활용했다. 5X5 보드를 uint32_t로 비트연산한 결과를 map에 저장하여 중복 탐색을 방지할 수 있었다.
uint32_t getState() {
uint32_t state = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == '*') {
int idx = i * 5 + j;
state |= (1u << idx);
}
}
}
return state;
}코드
비트 연산없이 완전탐색으로만 통과 (120ms)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int ans = 1e9;
char mat[6][6];
bool vis[6][6];
int d[4][2] = { {0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0} };
vector<pair<int, int>>v;
bool check() {
bool bfs[6][6];
int y, x;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == '*') {
y = i;
x = j;
}
bfs[i][j] = 0;
}
}
queue<pair<int, int>>q;
int count = 1;
q.push({ y,x });
bfs[y][x] = 1;
while (q.size()) {
int yy = q.front().first;
int xx = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if (count == v.size())
return 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int dy = yy + d[i][0];
int dx = xx + d[i][1];
if (dy >= 5 || dy < 0 || dx >= 5 || dx < 0)
continue;
if (bfs[dy][dx])
continue;
if (mat[dy][dx] == '*') {
q.push({ dy,dx });
bfs[dy][dx] = 1;
count++;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
void dfs(int idx, int cnt) {
if (idx == v.size()) {
if (check())
ans = min(ans, cnt);
return;
}
if (cnt >= ans) // 유망하지 않은 경우에는 탐색 X, 이 한줄로 실행시간이 많이 줄어들었다.
return;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
if (!vis[i][j]) {
vis[i][j] = 1;
mat[i][j] = '*';
int dis = abs(v[idx].first - i) + abs(v[idx].second - j);
dfs(idx + 1, cnt + dis);
mat[i][j] = '.';
vis[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
void solve() {
dfs(0, 0);
cout << ans;
}
void input() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cin >> mat[i];
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == '*') {
v.push_back({ i,j });
mat[i][j] = '.';
}
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
input();
solve();
}
비트연산으로 중복된 탐색을 제거 (128ms)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
int ans = 1e9;
char mat[6][6];
bool vis[6][6];
int d[4][2] = { {0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0} };
vector<pair<int, int>>v;
unordered_map<uint32_t,int>st;
bool check() {
bool bfs[6][6];
int y, x;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == '*') {
y = i;
x = j;
}
bfs[i][j] = 0;
}
}
queue<pair<int, int>>q;
int count = 1;
q.push({ y,x });
bfs[y][x] = 1;
while (q.size()) {
int yy = q.front().first;
int xx = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if (count == v.size())
return 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int dy = yy + d[i][0];
int dx = xx + d[i][1];
if (dy >= 5 || dy < 0 || dx >= 5 || dx < 0)
continue;
if (bfs[dy][dx])
continue;
if (mat[dy][dx] == '*') {
q.push({ dy,dx });
bfs[dy][dx] = 1;
count++;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
uint32_t getState() {
uint32_t state = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == '*') {
int idx = i * 5 + j;
state |= (1u << idx);
}
}
}
return state;
}
void dfs(int idx, int cnt) {
if (idx == v.size()) {
uint32_t state = getState();
if (st.count(state) && st[state] <= cnt) return;
st[state] = cnt;
if (check()) ans = min(ans, cnt);
return;
}
if (cnt >= ans)
return;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
if (!vis[i][j]) {
vis[i][j] = 1;
mat[i][j] = '*';
int dis = abs(v[idx].first - i) + abs(v[idx].second - j);
dfs(idx + 1, cnt + dis);
mat[i][j] = '.';
vis[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
void solve() {
dfs(0, 0);
cout << ans;
}
void input() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cin >> mat[i];
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == '*') {
v.push_back({ i,j });
mat[i][j] = '.';
}
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
input();
solve();
}마무리
완전 탐색으로 진행한 풀이가 이해가 더 쉽고 빨랐다. 하지만 map과 비트연산을 동시에 활용해볼 수 있는 문제였어서 비트마스킹을 활용해서도 풀이를 진행해봤다..
'백준 문제풀이 > dfs' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [BOJ] 24232 망가진 나무 (1) | 2025.11.07 |
|---|---|
| [BOJ] 23887 프린트 전달 (0) | 2025.10.19 |
| [BOJ] 14657 준오는 최종인재야!! (0) | 2025.10.05 |